Introduction to the Run Line
The Run command line may be one of the least utilized functions in the Start menu. This is a pity since it can be very useful. It is often the quickest way to launch programs or to open folders and documents. The figure below shows the Start-Run entry.
Clicking the entry "Run" opens the box shown below, where commands may be typed and entered.
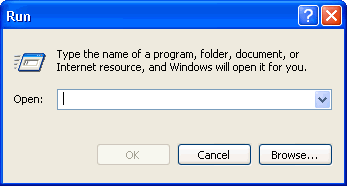
Opening applications in Run
Although applications can be opened in a variety of ways, the Run line often provides the quickest route. Desktop shortcut icons are also a quick route but you have to know how to create a shortcut for all the applications and you may end up with dozens of icons.
The best candidates for the Run line are applications that are in the "path" environment. (Go to this page for more discussion of the path.) The path environment is a set of folders whose names do not have to be included when entering a command. The path environment variable normally includes \Windows\ and \Windows\system32\. Many common accessories and Windows applets are in these folders and can be opened by entering just the executable file name. Several that I use constantly are the Registry editor (regedit) and the System Configuration Utility (msconfig). Note that neither of these frequently used system tools has an entry in Start- All Programs. The Run line is the standard method of accessing them.
A table listing some applications that can be opened in the Run line is given below.
| Entry for Run | Function |
|---|---|
| calc | Opens calculator |
| cmd | Opens command prompt window |
| explorer | Opens Windows explorer |
| magnify | Screen magnifier accessory |
| msconfig | System Configuration Utility |
| mshearts | Opens Hearts game |
| msinfo32 | System Information applet |
| mspaint | Opens graphics accessory Paint |
| notepad | Notepad accessory |
| regedit | Registry editor |
| sol | Opens Classical Solitaire game |
Programs not in the path require their full address, including the root folder and all subfolders. Actually typing long path names is not required since a "Browse" function comes with the Run line. This provides a way to search for files of interest and to enter them directly without typing. If desired, frequently used programs can be added to the path environment using the methods that are discussed in a section below.
Opening Management Consoles
Some of the functions that I find convenient to open by means of the Run line include various Management Consoles. For example, the disk defragmenter is opened by entering "dfrg.msc" . I find this easier than the multi-step process involved otherwise. A list of the appropriate file names for opening some of the various services is given in the table below. A more complete list is on this page.
| Entry for Run | Function |
|---|---|
| ciadv.msc | Manages the Indexing Service |
| compmgmt.msc | Computer Management Console. It contains a number of the other consoles |
| devmgmt.msc | Device Manager |
| dfrg.msc | Disk Defragmenter |
| diskmgmt.msc | Disk Management |
| gpedit.msc | Group Policy Editor. Windows XP Professional only |
| services.msc | Manages the many services involved in Windows and installed software |
The Source : http://commandwindows.com
'Operating System > Windosw' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Windows Command Line (0) | 2009.01.05 |
|---|---|
| Netstat [2] (0) | 2009.01.05 |
| GETMAC (0) | 2009.01.05 |
| Netstat (0) | 2009.01.05 |
| Widows Command Line (0) | 2009.01.05 |
